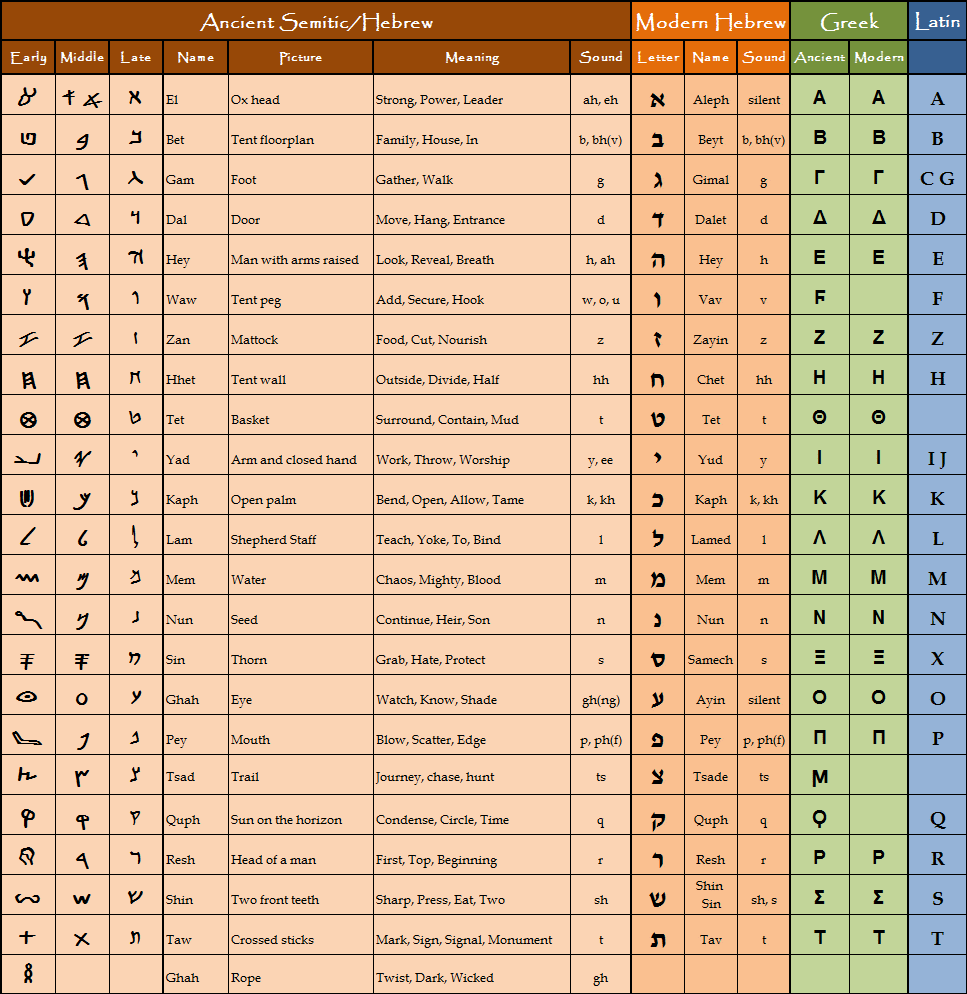
The Old Testament in Hebrew is a profound and ancient text that serves as the backbone of the Judeo-Christian tradition. Its verses resonate with theological significance, historical context, and literary beauty. For many, the Old Testament stands not just as a religious scripture but as a cultural artifact that has shaped the moral and ethical frameworks of societies throughout history. As readers delve into its Hebrew origins, they uncover layers of meaning that are often lost in translation, making the original language an essential aspect of understanding the text's richness.
In Hebrew, the Old Testament, known as the Tanakh, comprises three main sections: the Torah (Law), Nevi'im (Prophets), and Ketuvim (Writings). Each segment offers unique insights into the ancient world, reflecting the beliefs, customs, and struggles of its people. The beauty of the Hebrew language itself adds to the text's depth, with its intricate wordplay and poetic structures often revealing hidden messages and themes that might not be immediately apparent to non-Hebrew readers.
As we embark on a journey to explore the Old Testament in Hebrew, we will delve into its historical significance, linguistic features, and the impact it has had on modern interpretations of spirituality and morality. By examining the original texts, we can gain a more profound appreciation for this sacred scripture and its enduring influence on countless generations.
What is the Structure of the Old Testament in Hebrew?
The Old Testament in Hebrew is divided into three main sections:
- Torah: The first five books, also known as the Pentateuch, which include Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers, and Deuteronomy.
- Nevi'im: The section of the Hebrew Bible that includes the historical narratives and the prophetic books.
- Ketuvim: A collection of writings that encompasses poetry, philosophical texts, and historical accounts.
Why is the Hebrew Language Important for Understanding the Old Testament?
The Old Testament in Hebrew is crucial for a few reasons:
- Original Context: Understanding the Hebrew language allows readers to grasp the original context and nuances of the text that translations might overlook.
- Cultural Significance: The Hebrew language is deeply tied to Jewish culture and identity, providing insights into the societal norms and values of ancient Israel.
- Theological Depth: Many theological concepts in the Old Testament are expressed in unique ways in Hebrew, contributing to a richer understanding of key doctrines.
What Are the Challenges of Translating the Old Testament from Hebrew?
Translating the Old Testament from Hebrew comes with several challenges, including:
- Language Complexity: Hebrew has a different grammatical structure and vocabulary compared to English, making direct translations difficult.
- Idiomatic Expressions: Many Hebrew phrases do not have direct equivalents in other languages, leading to potential misinterpretation.
- Cultural References: Understanding the cultural context of the time is essential for accurate translation, which requires extensive knowledge of ancient customs and practices.
How Does the Old Testament in Hebrew Influence Modern Theology?
The Old Testament in Hebrew has profoundly influenced modern theology in various ways:
- Foundational Text: It serves as a foundational text for both Judaism and Christianity, shaping their theological frameworks and beliefs.
- Ethical Guidelines: The moral teachings found within the Old Testament continue to guide ethical discussions and decision-making in contemporary society.
- Interfaith Dialogue: The shared texts foster dialogue and understanding between different religious traditions, promoting a greater appreciation for the roots of faith.
What Literary Techniques Are Found in the Old Testament in Hebrew?
The Old Testament in Hebrew employs various literary techniques that enhance its message:
- Parallelism: Common in Hebrew poetry, this technique uses similar structures in successive lines to emphasize key ideas.
- Metaphor and Symbolism: Rich metaphors and symbols convey deeper meanings, inviting readers to contemplate the text beyond its literal interpretation.
- Chiasmus: A literary structure where concepts are presented in a mirrored format, creating a powerful effect that highlights central themes.
How Can One Study the Old Testament in Hebrew Effectively?
To study the Old Testament in Hebrew effectively, consider the following steps:
- Learn the Basics of Hebrew: Familiarize yourself with the Hebrew alphabet, grammar, and syntax to enhance comprehension.
- Utilize Commentaries: Use scholarly commentaries and resources that provide insights into the text's historical and cultural context.
- Join Study Groups: Engage with others interested in studying the Old Testament in Hebrew to share insights and interpretations.
- Practice Regularly: Regular practice with reading and translating Hebrew texts will improve fluency and understanding.
What Are Some Recommended Resources for Studying the Old Testament in Hebrew?
There are numerous resources available for those looking to study the Old Testament in Hebrew:
- Textbooks: Books such as "Basics of Biblical Hebrew" by Gary D. Pratico and Miles V. Van Pelt.
- Online Courses: Websites like Biblical Hebrew Online offer structured courses for learners.
- Hebrew Lexicons: Use lexicons to understand the meanings of Hebrew words and their usage in context.
- Study Bibles: Consider Bibles that include Hebrew texts alongside English translations for comparative study.
In conclusion, the Old Testament in Hebrew is a treasure trove of spiritual, historical, and cultural insights. By engaging with the text in its original language, readers can unlock a deeper understanding of its teachings and significance. Whether one is a scholar, a believer, or simply a curious reader, the journey into the Old Testament in Hebrew promises to be enlightening and enriching.