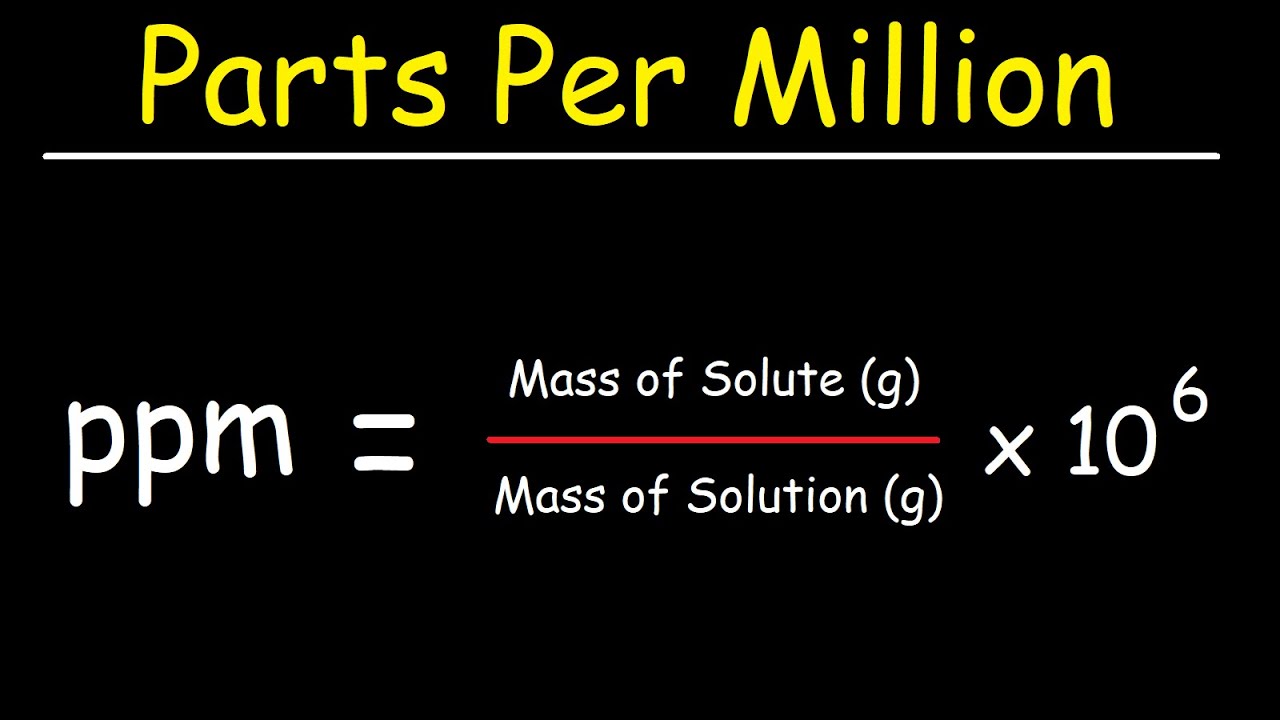In the world of science, technology, and industry, the term PPM stands out as a critical measurement that plays a significant role in various fields. Understanding what do you mean by PPM is essential for professionals and enthusiasts alike, as it helps in quantifying the presence of a substance in a given mixture. Whether you are dealing with environmental science, engineering, or manufacturing, PPM provides insights into the concentration levels of different materials. This article will delve into the significance of PPM, its applications, and how it affects our daily lives.
PPM, or parts per million, is a unit of measurement that denotes the concentration of one substance in a million parts of another. This measurement is particularly useful when dealing with very dilute solutions, as it allows for precise quantification of components that may exist in minuscule amounts. By grasping what do you mean by PPM, you can better appreciate its importance in various contexts, from assessing water quality to evaluating the purity of pharmaceuticals.
In addition to its scientific relevance, understanding PPM can have practical applications in everyday situations. For instance, if you're a consumer concerned about the safety of products you use or the air quality in your environment, knowing how to interpret PPM values can empower you to make informed decisions. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of PPM, exploring its definitions, uses, and implications in different industries.
What Is PPM?
PPM stands for parts per million, which is a measurement unit used to express very dilute concentrations of substances. It is especially common in fields such as chemistry, biology, and environmental science. One part per million indicates that there is one unit of a substance for every million units of the total solution or mixture. For example, if you have a solution containing 1 mg of a substance in 1 liter of water, this would equate to 1 PPM.
How Is PPM Calculated?
Calculating PPM can be done using a straightforward formula. The basic formula for finding PPM is:
PPM = (mass of solute / mass of solution) × 1,000,000
For instance, if a solution has 0.002 grams of a substance in 1,000 grams of solution, the calculation would be:
- PPM = (0.002 g / 1000 g) × 1,000,000 = 2 PPM
Where Is PPM Used?
PPM is utilized across various sectors, including:
- Environmental Monitoring: Measuring pollutants in air, water, and soil.
- Pharmaceuticals: Ensuring drug purity and safety.
- Food Industry: Assessing additives and contaminants.
- Manufacturing: Monitoring materials for quality control.
Why Is Understanding PPM Important?
Understanding what do you mean by PPM is crucial for several reasons:
- Health and Safety: PPM measurements can indicate potential health risks in contaminated environments.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries are required to meet specific PPM standards set by regulatory agencies.
- Quality Control: Ensuring product quality and safety through precise measurements.
What Are the Limitations of PPM?
While PPM is a useful measurement, it does have limitations:
- Context-Specific: PPM values can vary based on the context and the substances being measured.
- Not Always Comparable: Different substances may have different toxicological effects, making direct comparisons challenging.
How Does PPM Impact Environmental Policies?
PPM measurements play a significant role in shaping environmental policies. They help in:
- Establishing Safety Standards: Governments set PPM limits to protect public health.
- Monitoring Compliance: Organizations are monitored for adherence to PPM regulations.
What Do You Mean By PPM in Everyday Life?
In everyday life, PPM is more than just a scientific measurement. It influences:
- Product Labeling: Understanding ingredient concentrations in consumer products.
- Environmental Awareness: Being informed about air and water quality.
Can PPM Be Converted to Other Measurements?
Yes, PPM can be converted into other measurements such as percentage or milligrams per liter (mg/L). The conversion depends on the context and the specific substances involved. For example:
- 1 PPM = 1 mg/L for water solutions.
- To convert PPM to percentage: Percentage = PPM / 10,000.
Conclusion: Why Should You Care About PPM?
Understanding what do you mean by PPM is essential for anyone engaged in scientific research, industry practices, or even daily consumer choices. It equips you with the knowledge to interpret data accurately, ensuring safety and quality in various applications. As we continue to navigate a world where precision is paramount, PPM remains a vital tool in our quest for clarity and understanding in the measurements that shape our lives.