Understanding how to find acceleration is crucial for students, educators, and anyone interested in the world of physics and mechanics. Acceleration is not just a fundamental concept in physics; it is also a key element in various fields such as engineering, automotive industries, and even everyday life situations. In this article, we will explore the definition of acceleration, its formulas, how to calculate it, and its significance in real-world applications.
Whether you are a student preparing for exams or a professional seeking to refresh your knowledge, this guide will equip you with the necessary tools to understand and calculate acceleration effectively. We will delve into the different types of acceleration, provide examples, and explain how to apply these concepts practically. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how to find acceleration.
So, let’s embark on this journey to explore the fascinating world of acceleration, its calculations, and its applications!
Table of Contents
- What is Acceleration?
- Types of Acceleration
- The Formula for Acceleration
- How to Calculate Acceleration
- Examples of Acceleration in Real Life
- Importance of Understanding Acceleration
- Common Mistakes When Calculating Acceleration
- Conclusion
What is Acceleration?
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity of an object with respect to time. In simpler terms, it measures how quickly an object speeds up, slows down, or changes direction. The SI unit of acceleration is meters per second squared (m/s²).
Key points to remember about acceleration include:
- It can be positive (increasing speed) or negative (deceleration).
- Acceleration is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction.
- It is crucial for understanding motion in physics and engineering.
Types of Acceleration
There are several types of acceleration, each significant in different contexts. The primary types include:
- Uniform Acceleration: This occurs when an object accelerates at a constant rate.
- Variable Acceleration: Here, the acceleration changes over time.
- Centripetal Acceleration: This is the acceleration directed towards the center of a circular path.
- Angular Acceleration: This refers to the rate of change of angular velocity.
The Formula for Acceleration
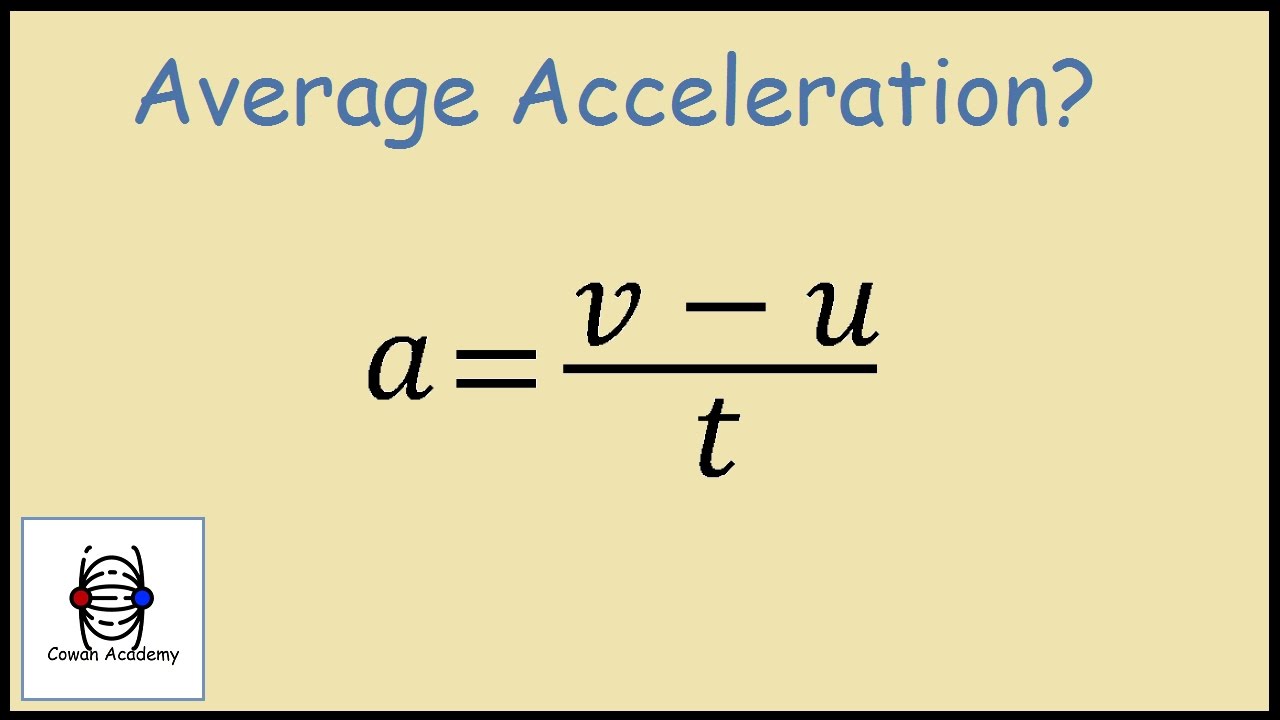
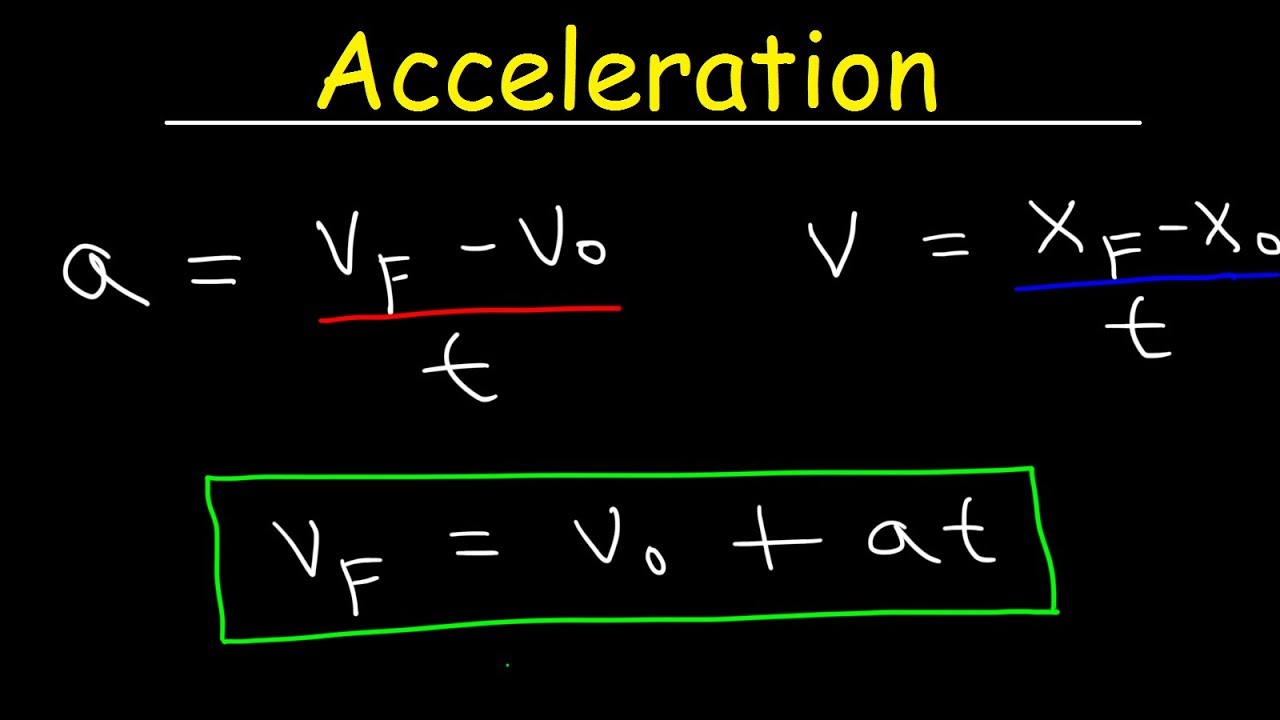
The basic formula to find acceleration (a) is derived from Newton's second law of motion:
a = (v_f - v_i) / t
Where:
- v_f: Final velocity
- v_i: Initial velocity
- t: Time taken for the change in velocity
Understanding the Formula
This formula indicates that acceleration is equal to the change in velocity divided by the time taken for that change. It helps quantify how fast an object is speeding up or slowing down.
How to Calculate Acceleration
Calculating acceleration involves a few simple steps:
- Identify the initial velocity (v_i) and the final velocity (v_f).
- Determine the time interval (t) over which the change occurs.
- Substitute these values into the acceleration formula.
Example Calculation
If a car's speed increases from 10 m/s to 30 m/s over a period of 5 seconds, the acceleration can be calculated as follows:
a = (30 m/s - 10 m/s) / 5 s = 4 m/s²
This means the car accelerates at a rate of 4 meters per second squared.
Examples of Acceleration in Real Life
Acceleration is not just a theoretical concept; it has practical applications in various fields:
- Automotive Industry: Understanding acceleration helps in designing vehicles for optimal performance.
- Aerospace Engineering: Acceleration is crucial in flight dynamics and spacecraft design.
- Sports: Athletes and trainers use acceleration metrics to improve performance.
- Physics Experiments: Acceleration is a key factor in motion experiments in educational settings.
Importance of Understanding Acceleration
Understanding acceleration is vital for several reasons:
- It is fundamental to the study of physics and engineering.
- It helps in designing safer vehicles and structures.
- It plays a crucial role in various sports and physical activities.
- It allows us to understand and predict the behavior of moving objects.
Common Mistakes When Calculating Acceleration
While calculating acceleration may seem straightforward, there are common pitfalls to avoid:
- Confusing acceleration with speed: Acceleration refers to the change in velocity, while speed is the magnitude of velocity.
- Neglecting the direction: Since acceleration is a vector, direction must always be considered.
- Incorrectly measuring time intervals: Ensure that the time is measured accurately to avoid errors in calculations.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding how to find acceleration is essential for anyone involved in physics, engineering, or related fields. We have explored what acceleration is, its different types, and how to calculate it using the appropriate formulas. By recognizing the importance of acceleration in real-life applications, you can appreciate its relevance in our world.
We encourage you to share your thoughts in the comments below, explore other articles on our site, and continue learning about the fascinating world of physics!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back again for more insightful content!