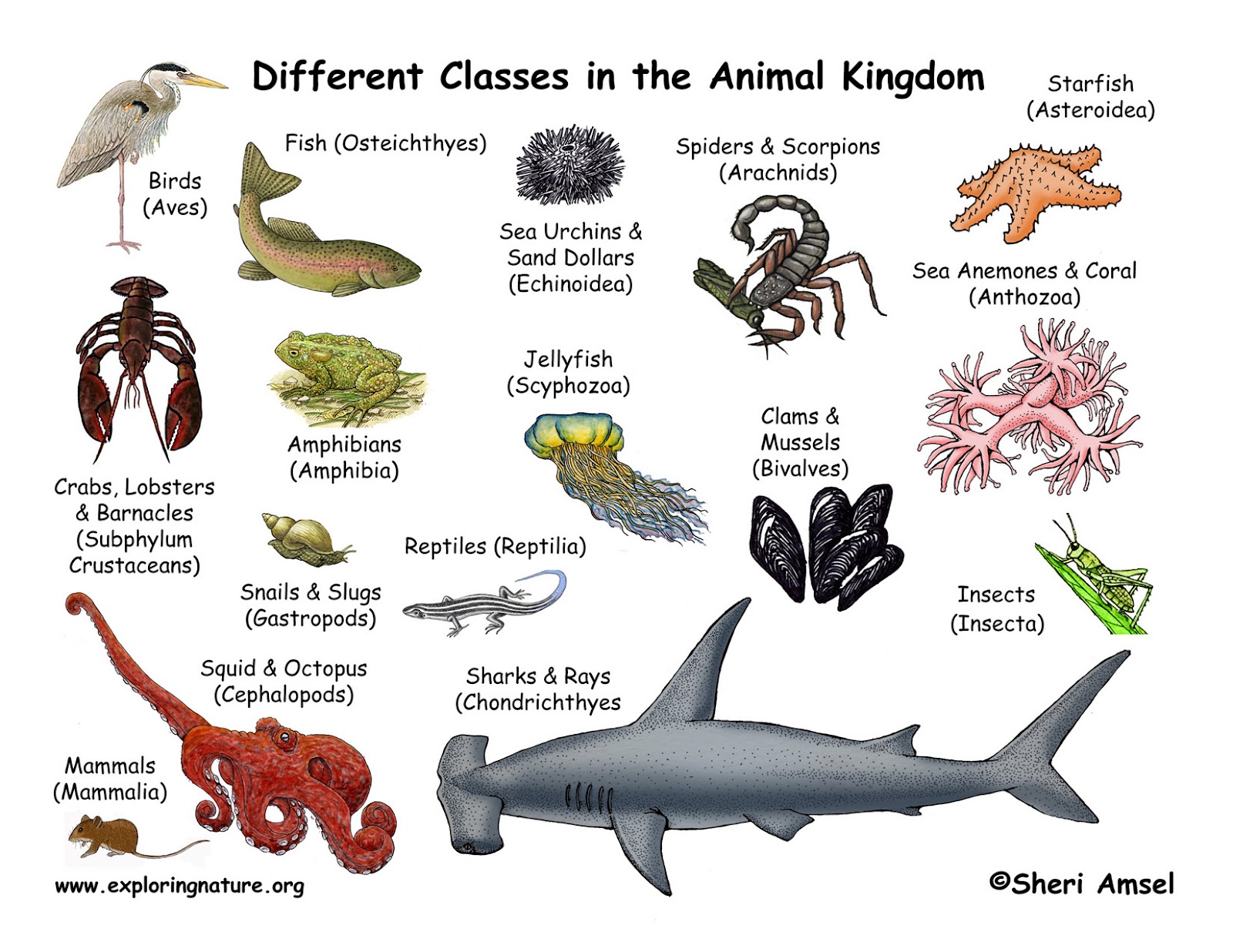
Understanding the characteristics of organisms within various species is vital for anyone interested in biology, ecology, or environmental science. These characteristics not only define the organism's role within its ecosystem but also influence its behavior, reproduction, and survival strategies. In this article, we will delve into the specific attributes that distinguish organisms within different species, providing insights into their adaptations, habitats, and interactions with other species.
By examining the characteristics of specific organisms, we can better understand biodiversity and the evolutionary processes that shape life on Earth. From the smallest microorganisms to the largest mammals, each organism displays unique traits that contribute to the overall balance of their environments. This comprehensive exploration will highlight the importance of these characteristics in understanding ecological relationships and conservation efforts.
This article will cover various aspects of organismal characteristics, including morphology, behavior, physiology, and genetic diversity. We aim to provide a thorough understanding of how these attributes influence the survival and success of different species in their respective habitats.
Table of Contents
- Morphological Characteristics
- Behavioral Characteristics
- Physiological Characteristics
- Genetic Diversity
- Habitat-Specific Adaptations
- Interactions with Other Species
- Importance of Characteristics in Conservation
- Conclusion
Morphological Characteristics
Morphological characteristics refer to the physical traits of organisms, including size, shape, color, and structural features. These characteristics can vary significantly among species and can provide insights into their ecological roles and evolutionary history.
- Size and Shape: The size of an organism can impact its ability to access resources and evade predators. For example, smaller insects may thrive in dense vegetation where larger animals cannot navigate.
- Coloration: Many organisms use coloration for camouflage, mating displays, or warning signals. Bright colors may indicate toxicity, while muted tones can help with blending into the environment.
- Structural Features: Unique physical adaptations, such as the elongated neck of a giraffe or the webbed feet of a duck, allow organisms to exploit their environments effectively.
Behavioral Characteristics
Behavioral characteristics encompass the actions and responses of organisms to their environment. These behaviors are crucial for survival, reproduction, and social interactions.
- Foraging Behavior: Different species have developed various foraging strategies to obtain food, such as hunting, scavenging, or gathering.
- Mating Rituals: Many species exhibit unique mating behaviors, which can include elaborate courtship displays or competitive interactions among males.
- Social Structures: Some organisms live in complex social groups, while others are solitary. Social behaviors can affect mating success, resource allocation, and protection against predators.
Physiological Characteristics
Physiological characteristics refer to the internal processes and functions that enable organisms to survive in their environments. These characteristics can include metabolic rates, reproductive strategies, and adaptations to environmental stressors.
- Metabolic Rates: Different species exhibit varying metabolic rates, influencing their energy requirements and activity levels.
- Reproductive Strategies: Organisms may reproduce sexually or asexually, with strategies that can include high offspring numbers or extended parental care.
- Adaptations to Stress: Many organisms have developed physiological adaptations to cope with extreme environments, such as drought-resistant plants or cold-adapted animals.
Genetic Diversity
Genetic diversity within and between species is essential for resilience and adaptability. A higher level of genetic variation can enhance the ability of populations to survive environmental changes and resist diseases.
- Importance of Genetic Variation: Populations with greater genetic diversity are often more robust and capable of adapting to shifting conditions.
- Inbreeding and Its Effects: Low genetic diversity can lead to inbreeding depression, reducing fitness and increasing vulnerability to environmental changes.
Habitat-Specific Adaptations
Organisms exhibit specific adaptations that enable them to thrive in their particular habitats, whether terrestrial, aquatic, or aerial. Understanding these adaptations is crucial for conservation efforts and habitat management.
- Terrestrial Adaptations: Animals and plants in terrestrial environments may develop drought resistance or adaptations to avoid herbivory.
- Aquatic Adaptations: Aquatic organisms often have adaptations such as streamlined bodies for efficient swimming or specialized respiratory systems for underwater breathing.
Interactions with Other Species
The characteristics of organisms are often shaped by their interactions with other species, which can include competition, predation, and symbiosis. These relationships are critical for maintaining ecosystem balance.
- Competition: Organisms may compete for resources such as food, space, or mates, influencing their growth and reproduction.
- Predation: Predator-prey relationships drive evolutionary adaptations in both predators and their prey, leading to a dynamic balance within ecosystems.
- Symbiosis: Many organisms engage in symbiotic relationships, where two species interact closely and benefit from one another, such as pollinators and flowers.
Importance of Characteristics in Conservation
Understanding the characteristics of organisms is essential for effective conservation strategies. By recognizing how these traits influence survival and reproduction, conservationists can develop targeted efforts to protect vulnerable species and their habitats.
- Habitat Preservation: Protecting habitats that support specific organism characteristics is crucial for maintaining biodiversity.
- Species Recovery Plans: Knowledge of species-specific characteristics can inform recovery plans for endangered species.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the characteristics of organisms within species play a fundamental role in their survival, reproduction, and interactions with their environments. By exploring morphological, behavioral, physiological, and genetic traits, we can gain a deeper understanding of biodiversity and the complexities of ecosystems. We encourage readers to engage with this topic further and share their thoughts in the comments section below.
We hope you found this article informative and insightful. If you enjoyed reading about the characteristics of this organism in species, please consider sharing it with others or exploring more articles on our website.