Peaked T waves are an essential aspect of electrocardiogram (ECG) interpretation that can indicate various cardiac conditions. These distinctive waveforms can provide crucial insights into a patient's heart health and are vital for healthcare professionals to recognize during routine examinations. In this article, we will delve deep into the topic of peaked T waves, exploring their significance, characteristics, and the possible underlying conditions they may indicate. Whether you are a medical student, healthcare provider, or simply interested in understanding more about cardiac health, this article will serve as a thorough resource.
Understanding peaked T waves requires a foundational knowledge of ECG interpretation, as these waves are an integral part of the heart's electrical activity. The T wave represents the repolarization of the ventricles, and any abnormalities in its shape can signify underlying health issues. This guide will help you navigate through the complexities surrounding peaked T waves and arm you with the knowledge to identify and understand their implications.
In the following sections, we will cover the definition of peaked T waves, their clinical significance, the various conditions associated with them, and the steps necessary for proper diagnosis and treatment. Alongside, we will also address frequently asked questions to enhance your understanding of this critical topic.
Table of Contents
- 1. Definition of Peaked T Waves
- 2. Characteristics of Peaked T Waves
- 3. Clinical Significance of Peaked T Waves
- 4. Conditions Associated with Peaked T Waves
- 4.1 Hyperkalemia
- 4.2 Ischemic Heart Disease
- 4.3 Ventricular Hypertrophy
- 4.4 Central Nervous System Issues
- 5. Diagnosis of Peaked T Waves
- 6. Treatment Options
- 7. Frequently Asked Questions
- 8. Conclusion
1. Definition of Peaked T Waves
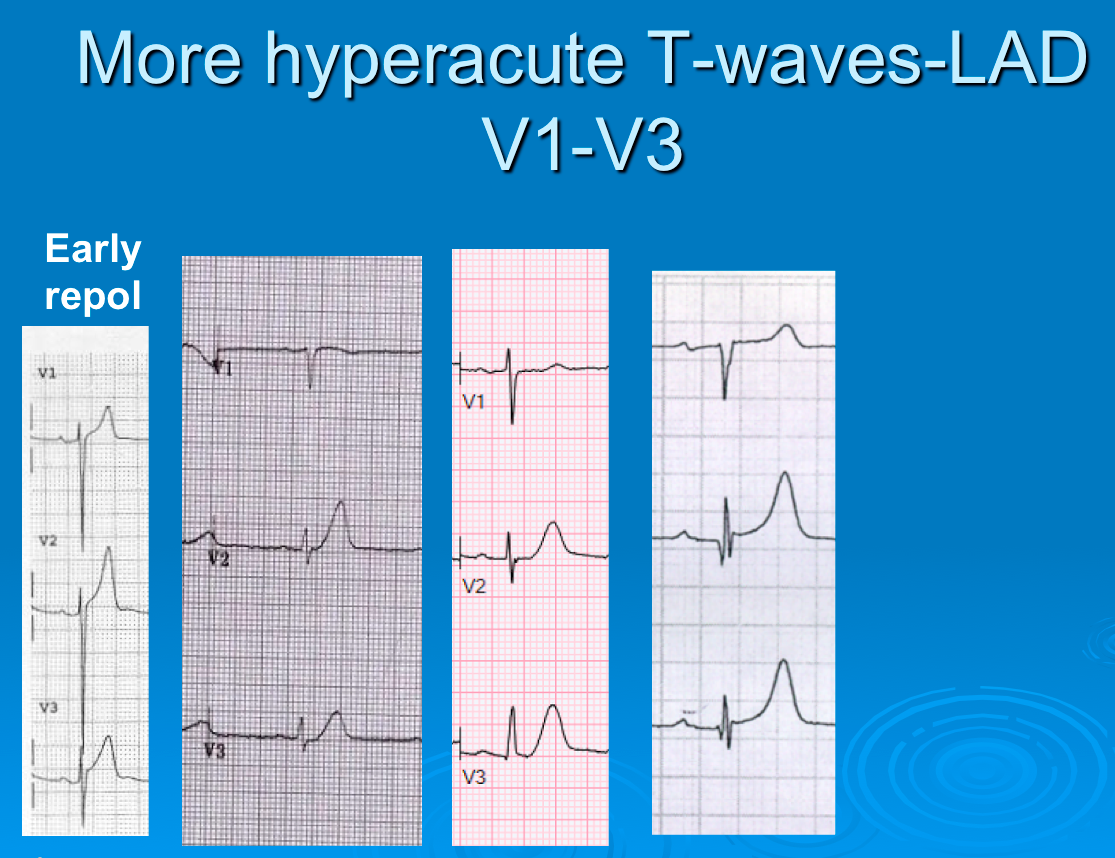
Peaked T waves are defined as tall, pointed T waves that are typically more pronounced than the normal T wave morphology observed on an ECG. These waves can vary significantly in height and width, but they are characterized by their sharp peaks. Recognizing these waves is crucial for healthcare providers as they often signal an underlying issue that may require further investigation.
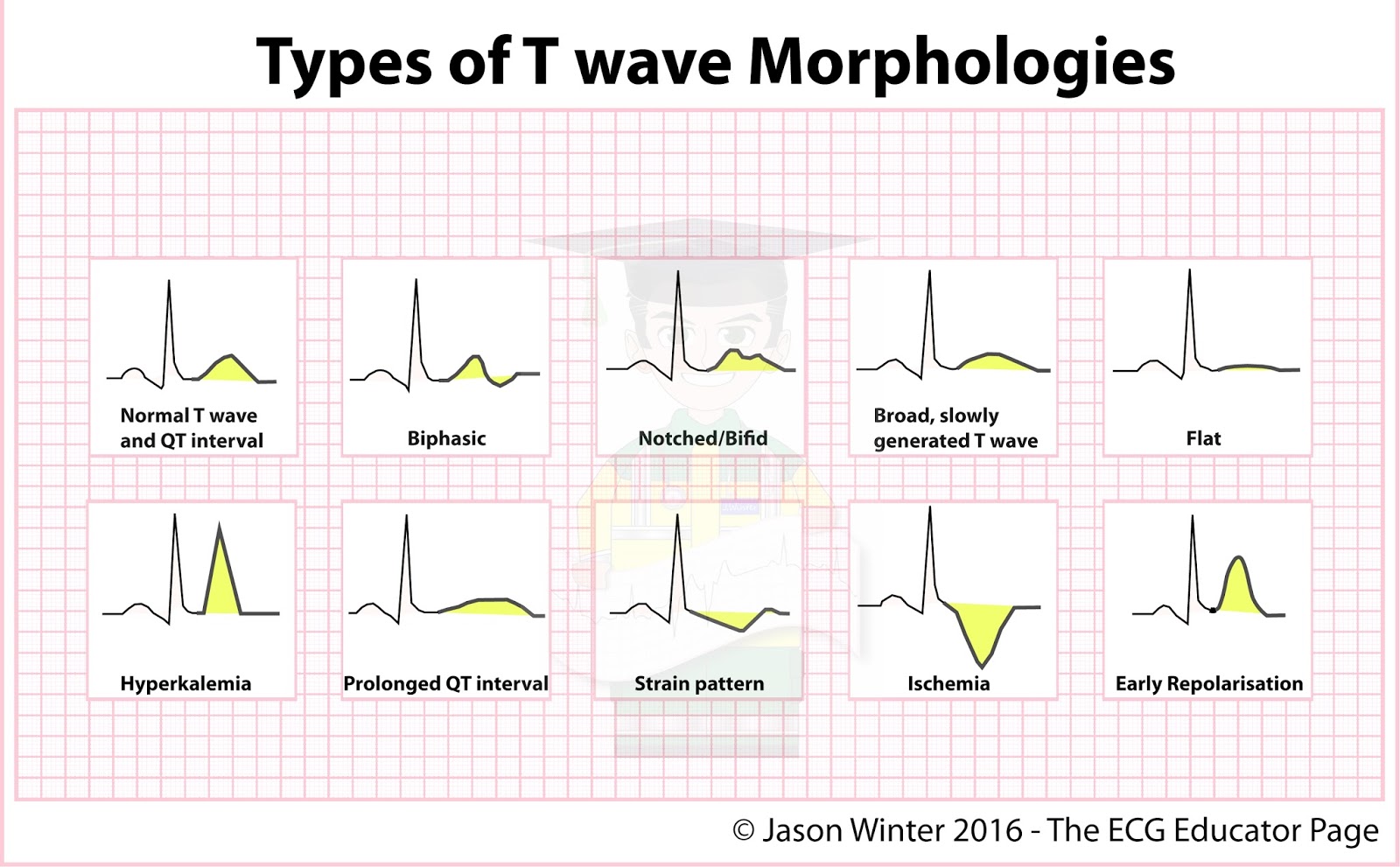
2. Characteristics of Peaked T Waves
The characteristics of peaked T waves include:
- Height: Peaked T waves are usually taller than normal T waves, often exceeding 5 mm in height in the precordial leads.
- Shape: The shape is pointed, making it easily distinguishable from the typical rounded T wave.
- Lead Variation: Peaked T waves may appear in specific leads, often in the anterior and lateral leads of the ECG.
3. Clinical Significance of Peaked T Waves
Peaked T waves are clinically significant as they can indicate various cardiac and non-cardiac conditions. Their presence can guide healthcare professionals in diagnosing conditions that may require immediate attention. Some of the most common implications of peaked T waves include:
- Potential myocardial infarction.
- Electrolyte imbalances, particularly hyperkalemia.
- Cardiac strain or hypertrophy.
4. Conditions Associated with Peaked T Waves
Several medical conditions can lead to the presence of peaked T waves on an ECG. Understanding these conditions is vital to providing appropriate care.
4.1 Hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia, an elevated level of potassium in the blood, is one of the most common causes of peaked T waves. The relationship between potassium levels and T wave morphology is well established, with peaked T waves often serving as a warning sign of potassium dysregulation.
4.2 Ischemic Heart Disease
Ischemic heart disease, characterized by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, can also manifest peaked T waves. During a myocardial infarction, for instance, changes in the T wave morphology may indicate ischemia or infarction.
4.3 Ventricular Hypertrophy
Ventricular hypertrophy, or thickening of the heart's ventricular walls, can lead to changes in the ECG that result in peaked T waves. This condition often arises from long-standing hypertension or heart valve disease.
4.4 Central Nervous System Issues
In addition to cardiac causes, peaked T waves can also be associated with certain central nervous system issues, such as increased intracranial pressure. This highlights the importance of a comprehensive evaluation when peaked T waves are identified on an ECG.
5. Diagnosis of Peaked T Waves
Diagnosing peaked T waves involves a thorough review of the patient's medical history, physical examination, and ECG interpretation. Healthcare providers must consider the patient's symptoms, risk factors, and any underlying conditions that may contribute to the presence of these abnormal waves. Additional tests, such as blood tests to assess electrolyte levels, may also be necessary to determine the underlying cause.
6. Treatment Options
Treatment for peaked T waves primarily focuses on addressing the underlying cause. Depending on the specific condition identified, treatment options may include:
- Medications to correct electrolyte imbalances.
- Interventions for ischemic heart disease, such as angioplasty or medication management.
- Lifestyle modifications to manage hypertension or other contributing factors.
7. Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions regarding peaked T waves:
- What other ECG changes can accompany peaked T waves? Other changes may include ST segment elevation or depression, which can provide further context to the cardiac condition.
- Are peaked T waves always a sign of a serious condition? Not necessarily; they can indicate various issues, some of which may not be immediately life-threatening.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, peaked T waves are a critical component of ECG interpretation that can reveal important information about a patient's heart health. Understanding their characteristics and clinical significance is essential for healthcare providers in diagnosing and managing various conditions. If you notice any unusual symptoms or have concerns about your heart health, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
Feel free to leave your comments below or share this article with others who may find it useful. For more informative articles, be sure to explore our website!
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to seeing you again soon!