The study of the elements of compounds is fundamental to the field of chemistry, providing insights into how different substances interact and combine. Compounds, which are substances formed when two or more elements bond together, are all around us, from the water we drink to the air we breathe. Understanding the elements that make up these compounds is crucial for both scientific research and everyday life.
In this article, we will explore the various aspects of compounds and their components, including the types of elements involved, the properties of compounds, and the significance of these elements in various applications. Whether you are a student learning chemistry or simply curious about the world around you, this guide will provide valuable information on the elements of compounds.
Furthermore, we will delve into the importance of understanding chemical compounds in fields such as medicine, environmental science, and engineering, showcasing their impact on our daily lives. Join us as we unravel the complexities of the elements that form the compounds essential to our existence.
Table of Contents
- What Are Elements?
- What Are Compounds?
- Types of Elements in Compounds
- Properties of Compounds
- Importance of Compounds
- Applications of Compounds
- Common Compounds
- Conclusion
What Are Elements?
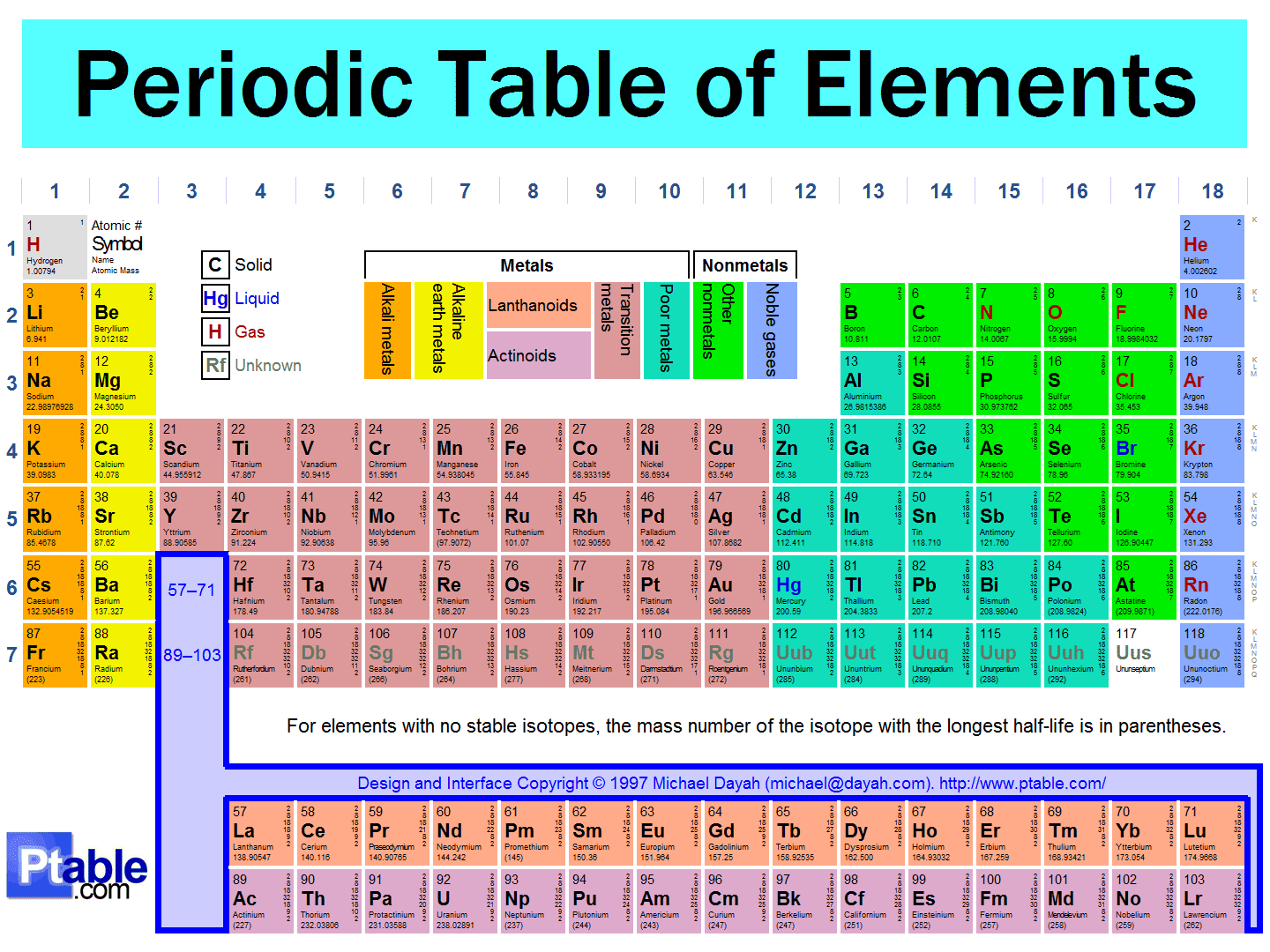
Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Each element is made up of atoms that have the same number of protons in their nuclei, which defines their chemical properties. The periodic table organizes all known elements, providing information about their atomic structure and characteristics.
There are currently 118 known elements, each represented by a unique symbol. For example, hydrogen is denoted as "H," while oxygen is represented as "O." Elements can be classified into metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, each with distinct properties and behaviors.
What Are Compounds?
Compounds are substances formed when two or more elements chemically bond together. The properties of compounds are often very different from those of the elements that make them up. For instance, sodium (Na) is a highly reactive metal, and chlorine (Cl) is a poisonous gas; however, when they combine, they form sodium chloride (NaCl), commonly known as table salt, which is safe to consume.
Compounds can be classified into two main categories: ionic compounds and covalent compounds. Ionic compounds are formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of charged ions. Covalent compounds, on the other hand, are formed when atoms share electrons.
Types of Elements in Compounds
Compounds are primarily composed of two types of elements: metallic and nonmetallic elements. Understanding the role of each type of element in compound formation is essential for grasping the fundamentals of chemistry.
Metallic Elements
Metallic elements, such as iron, copper, and aluminum, typically exhibit properties like conductivity, malleability, and ductility. These elements tend to lose electrons and form positive ions, which allows them to participate in ionic bonding.
Nonmetallic Elements
Nonmetallic elements, such as oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur, usually have properties that are opposite to those of metals. They tend to gain electrons and form negative ions or share electrons when forming covalent bonds. Nonmetals play a crucial role in the formation of various compounds, particularly organic compounds essential for life.
Properties of Compounds
The properties of compounds are determined by the types of elements involved and the nature of the bonds that hold the elements together. Understanding these properties is vital for predicting how compounds will behave in different situations.
Physical Properties
- Melting and boiling points: Compounds can have varying melting and boiling points, depending on the strength of the bonds between their constituent atoms.
- Solubility: Some compounds dissolve easily in water, while others do not. This property is significant in chemical reactions and biological processes.
- Color and appearance: The visual characteristics of a compound can provide clues about its composition and structure.
Chemical Properties
- Reactivity: Some compounds are highly reactive, while others are stable and unreactive.
- Acidity and basicity: Compounds can be classified as acids, bases, or neutral, influencing their behavior in chemical reactions.
- Oxidation states: The oxidation state of the elements in a compound can affect its reactivity and stability.
Importance of Compounds
Compounds play a crucial role in various aspects of life, including biological processes, industrial applications, and environmental science. Understanding the elements that make up these compounds allows scientists to develop new materials, medicines, and technologies.
For instance, compounds are essential in biochemistry, where they form the basis of DNA, proteins, and enzymes. In industrial applications, compounds are used in manufacturing, agriculture, and energy production. Additionally, compounds play a significant role in environmental science, helping researchers understand pollution and its effects on ecosystems.
Applications of Compounds
The applications of compounds are vast and varied, impacting our lives in numerous ways. Here are some key areas where compounds are utilized:
- Medicine: Many pharmaceuticals are compounds that interact with biological systems to treat diseases.
- Food industry: Compounds such as preservatives and flavor enhancers are used to improve food quality and safety.
- Materials science: Compounds are crucial in developing new materials with specific properties for various applications.
- Environmental science: Understanding the compounds in pollutants helps in developing strategies for pollution control and remediation.
Common Compounds
Several compounds are frequently encountered in everyday life. Here are some examples:
- Water (H2O): A vital compound for all known forms of life.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): A compound produced during respiration and combustion, essential for photosynthesis.
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl): Common table salt, used in cooking and food preservation.
- Glucose (C6H12O6): A simple sugar that serves as an energy source for living organisms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the elements of compounds are fundamental to our understanding of chemistry and the natural world. By exploring the types of elements involved in compound formation, their properties, and their applications, we gain valuable insights into the substances that make up our environment.
We encourage you to delve deeper into the fascinating world of compounds and their elements. Share your thoughts in the comments section below, and don’t forget to explore our other articles for more information on related topics!
References
- Atkins, P. W., & Jones, L. (2010). Chemical Principles: The Quest for Insight. W. H. Freeman and Company.
- Zumdahl, S. S., & Zumdahl, S. A. (2014). Chemistry. Cengage Learning.
- Burdge, J. (2016). Chemistry. McGraw-Hill Education.