Plant and animal cells are the fundamental building blocks of all living organisms. Understanding their structure and function is crucial for anyone studying biology or related fields. This article delves deep into the differences and similarities between plant and animal cells, exploring their components, functions, and significance in the broader context of life on Earth.
In this guide, we will cover essential topics such as the unique features of plant cells, the characteristics of animal cells, and how these differences impact their roles in various biological processes. Whether you're a student, educator, or simply curious about biology, this article aims to provide valuable insights and information.
As we explore the intricate world of cells, we will incorporate relevant data, statistics, and trustworthy sources to ensure a well-rounded understanding. Let’s embark on this journey of discovery into the fascinating realm of plant and animal cells.
Table of Contents
- Biography of Plant and Animal Cells
- Data and Biodata
- Structure of Plant and Animal Cells
- Key Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells
- Functions of Plant and Animal Cells
- Importance of Plant and Animal Cells
- Recent Research and Discoveries
- Conclusion
Biography of Plant and Animal Cells
Plant and animal cells have distinct histories that date back billions of years to the earliest forms of life on Earth. They are categorized as eukaryotic cells, which means they possess a nucleus and specialized organelles. This classification places them within a larger group known as eukaryotes, which also includes fungi and protists.
Data and Biodata
| Feature | Plant Cells | Animal Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Present | Absent |
| Chloroplasts | Present | Absent |
| Vacuoles | Large central vacuole | Small, if present |
| Shape | Typically rectangular | Irregular shape |
| Energy Storage | Starch | Glycogen |
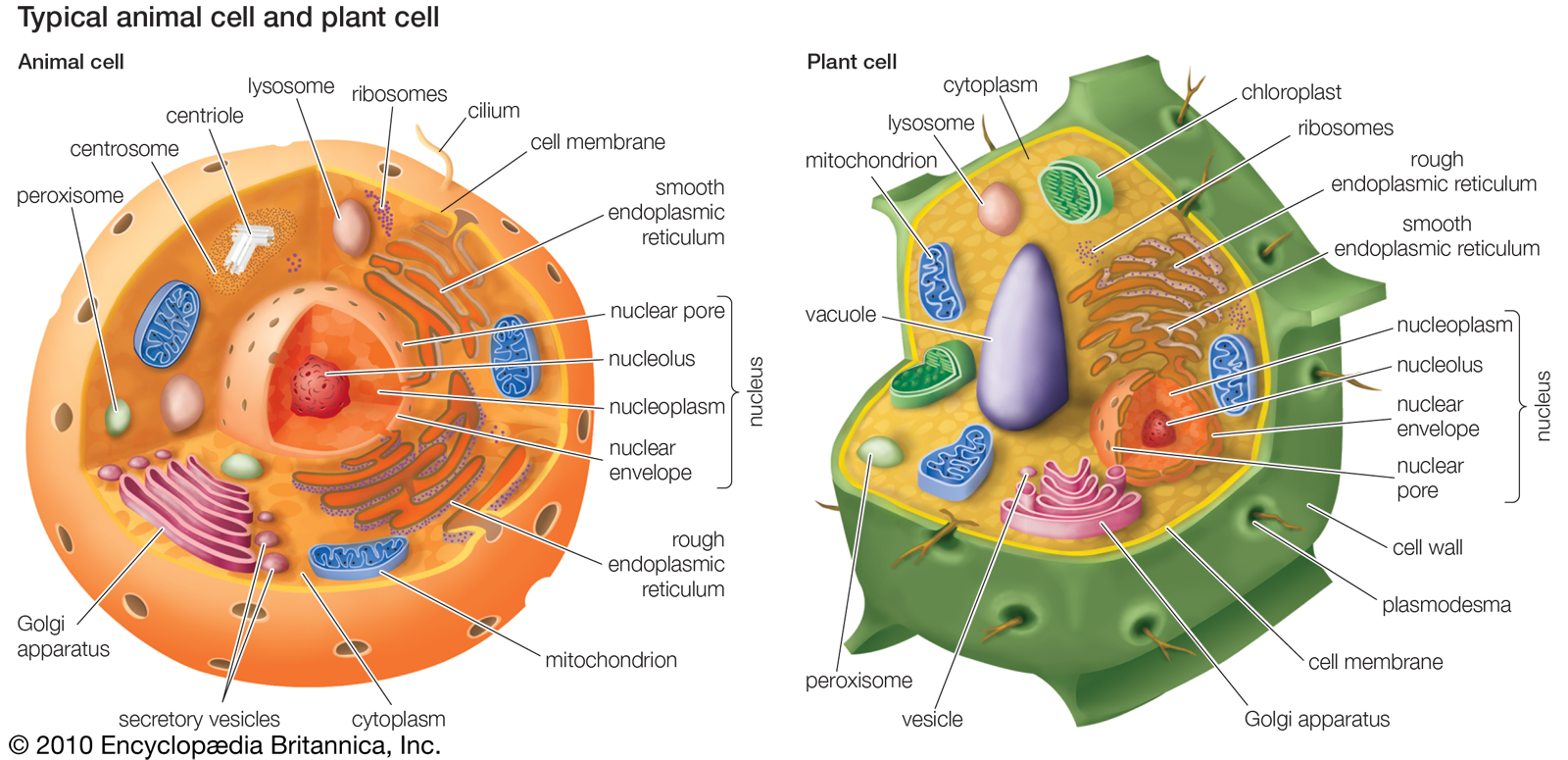
Structure of Plant and Animal Cells
The structure of plant and animal cells varies significantly, reflecting their different functions and roles in living organisms.
Components of Plant Cells
- Cell Wall: Provides structural support and protection.
- Chloroplasts: Site of photosynthesis, allowing plants to convert sunlight into energy.
- Large Vacuole: Stores nutrients, waste products, and helps maintain turgor pressure.
- Plasma Membrane: Regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Components of Animal Cells
- Cell Membrane: Acts as a barrier and regulates what enters and exits the cell.
- Mitochondria: Powerhouse of the cell, generating energy through respiration.
- Centrioles: Involved in cell division and the organization of the mitotic spindle.
- Lysosomes: Contain enzymes for digestion and waste disposal.
Key Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells
Understanding the differences between plant and animal cells helps clarify their unique roles in the ecosystem.
- Cell Wall: Plant cells have a rigid cell wall made of cellulose, while animal cells do not.
- Chloroplasts: Only plant cells contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
- Vacuoles: Plant cells typically have one large central vacuole, while animal cells may have smaller vacuoles.
- Shape: Plant cells are generally more rectangular, while animal cells tend to be irregularly shaped.
Functions of Plant and Animal Cells
Both plant and animal cells perform vital functions that contribute to the survival and growth of organisms.
Functions of Plant Cells
- Photosynthesis: Captures sunlight to produce energy and oxygen.
- Storage: Stores nutrients and waste products in vacuoles.
- Support: Maintains structure and rigidity through the cell wall.
Functions of Animal Cells
- Respiration: Converts food into energy in mitochondria.
- Movement: Enables organism movement through muscle and nerve cells.
- Communication: Uses signaling molecules to communicate with other cells.
Importance of Plant and Animal Cells
Both plant and animal cells are essential to the functioning of ecosystems and the overall health of the planet.
- Plant cells produce oxygen and organic matter through photosynthesis, supporting life on Earth.
- Animal cells contribute to biodiversity and the balance of ecosystems.
- Understanding cell biology is crucial for advancements in medicine, agriculture, and environmental conservation.
Recent Research and Discoveries
Recent studies have shed light on the complexities of plant and animal cells, revealing new insights into their functions and potential applications in science.
- Research in genetically modified organisms (GMOs) aims to enhance crop yield and resistance to pests.
- Stem cell research is exploring the potential for regenerative medicine and treating diseases.
- Studies on cellular communication are paving the way for innovations in medical treatments.
Conclusion
In summary, plant and animal cells are fundamental to the existence of life on Earth. Their unique structures and functions play crucial roles in maintaining the balance of ecosystems and supporting biological processes. By understanding these cells better, we can appreciate the complexity of life and the importance of cellular biology in various fields.
We encourage you to leave your thoughts in the comments below, share this article with others, or explore more articles on our site to deepen your understanding of biology.
Penutup
Thank you for joining us on this exploration of plant and animal cells. We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights and knowledge. We invite you to return for more informative content in the future!
/animal-cells-vs-plant-cells-373375_final-5b462d7fc9e77c00375014f1.png)